
AML Initiative
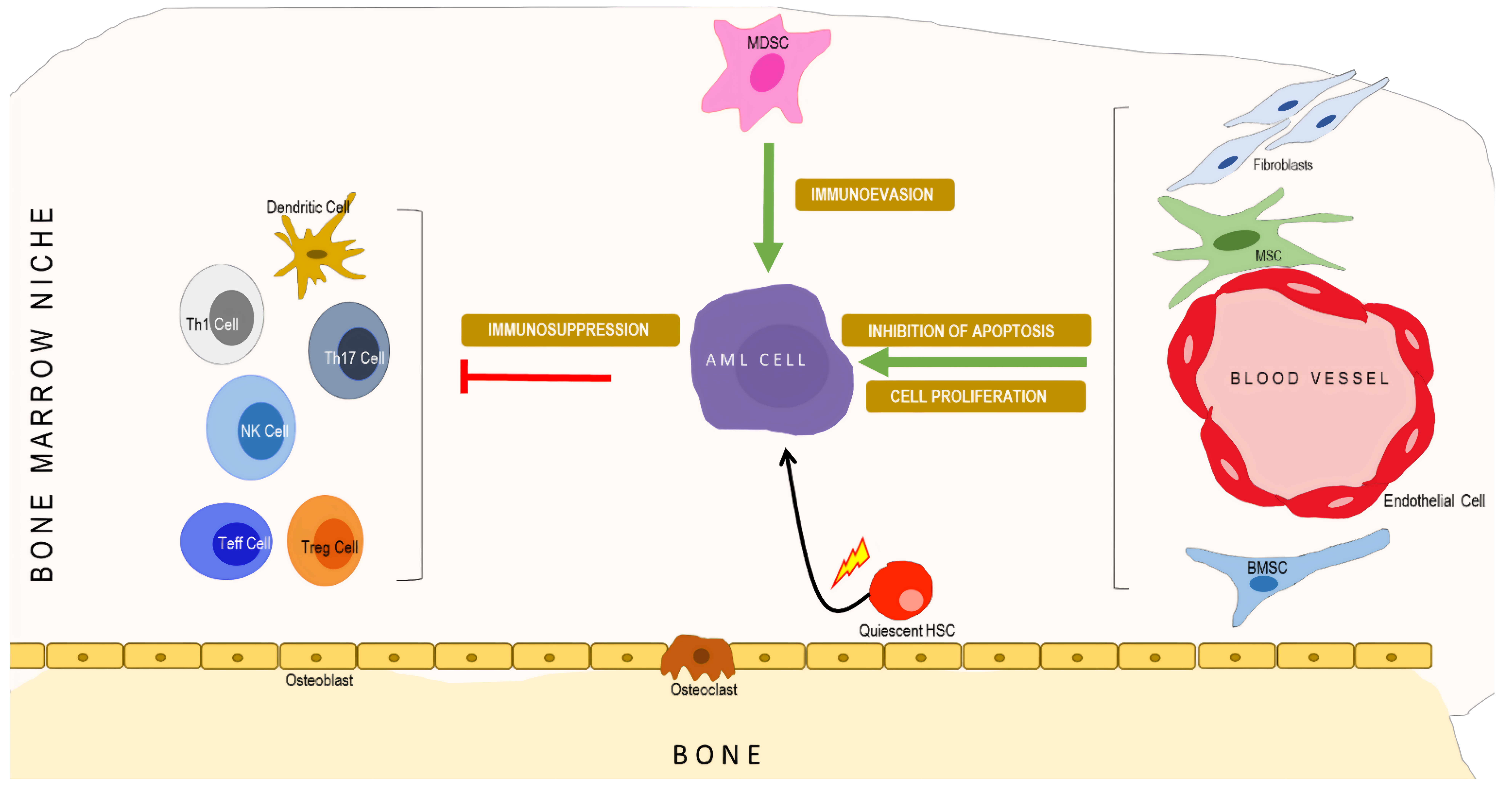
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) is a fast-progressing cancer of the blood and bone marrow, characterized by the abnormal proliferation of myeloid cells. These cancerous cells hinder the production of healthy blood cells, leading to anemia, infections, and bleeding complications. AML primarily affects older adults, with a higher incidence in individuals over 60 years. It is the most common type of acute leukemia in adults, accounting for about 1% of all cancers globally. The disease progresses rapidly, requiring immediate medical attention. Despite advancements in chemotherapy, stem cell transplants, and targeted therapies, AML remains challenging to treat due to high relapse rates. Early diagnosis and personalized treatment approaches are crucial for improving patient outcomes.
Research Progress
The Open Science Institute’s AML initiative project has progressed now to the Third stage of In silico Modeling. Our goal is to raise $750,000 to go perform in silico modeling and provide the revolutionary soution for AML. Please support this initiative.
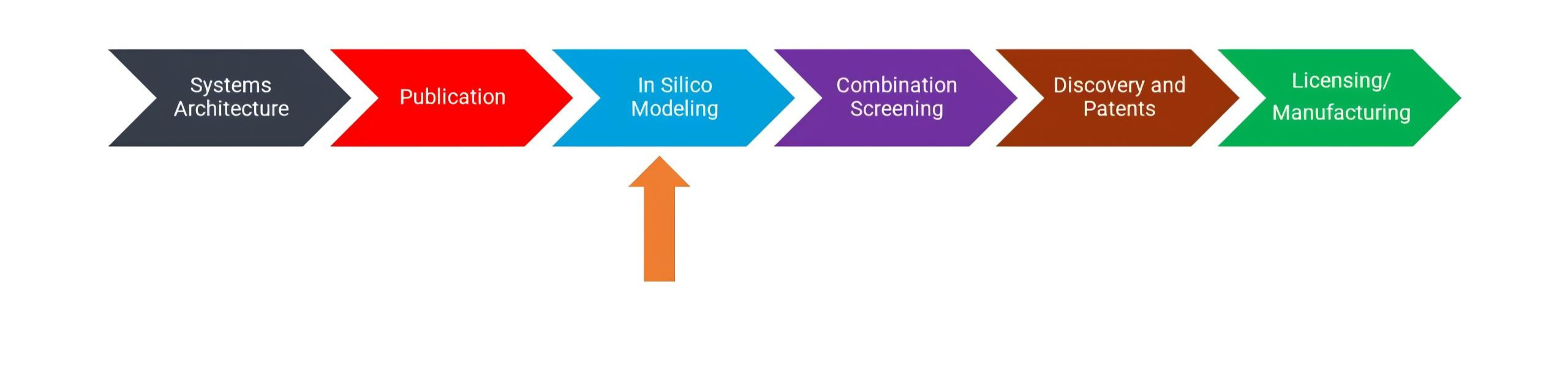
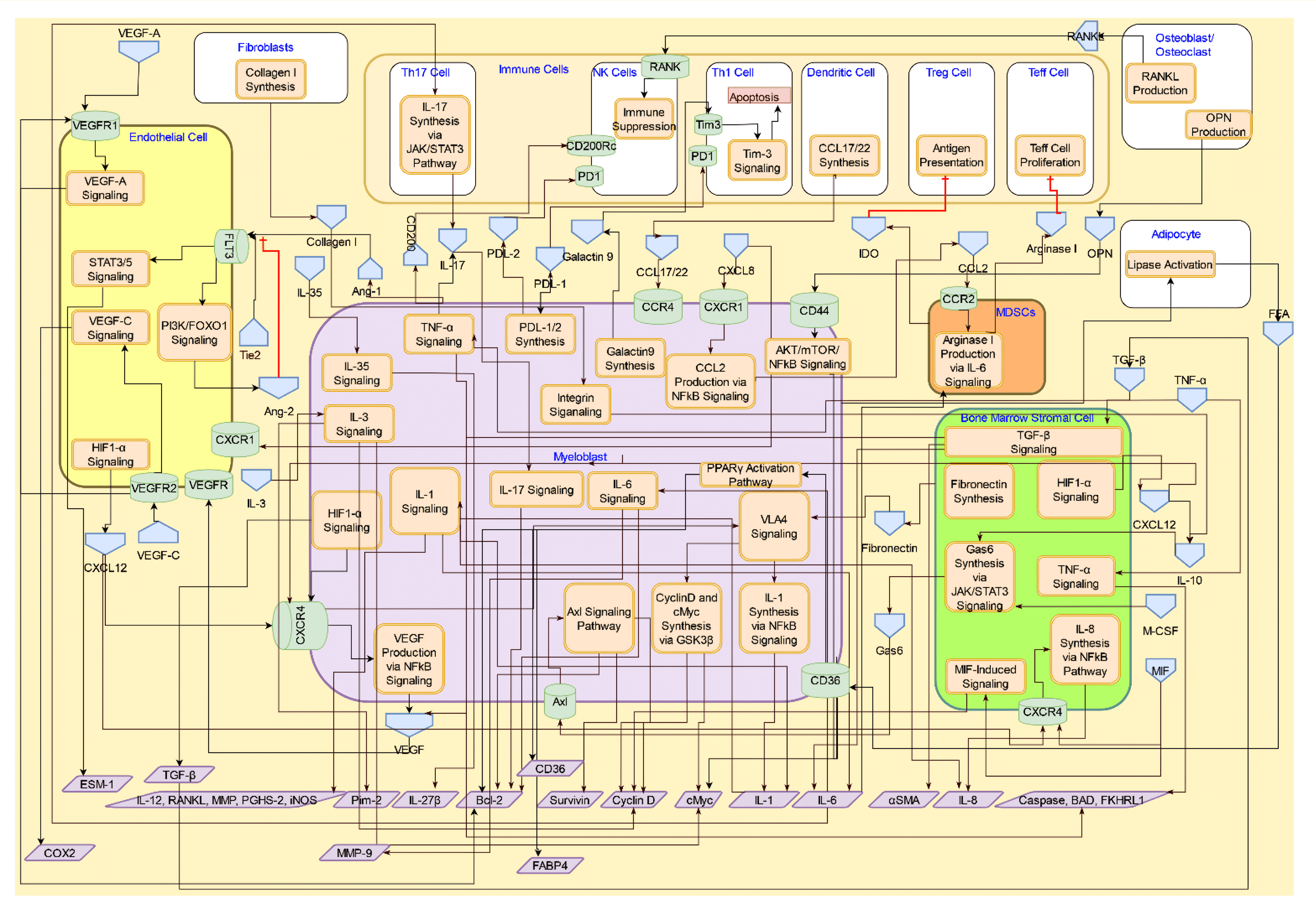
Systems Architecture
The Systems Architecture of AML is published as a web based tool open to public. Click below to interact with the Systems Architecture.
Publication
A peer-reviewed publication resulting from the work of AML initiative was published in 2021 in the Cancers Journal. Download the paper below

In Silico Modeling
In this phase, the AML Initiative will conduct in silico modeling to identify and test the efficacy of natural ingredients on immunosuppression and cell proliferation activity. This phase is yet to begin.
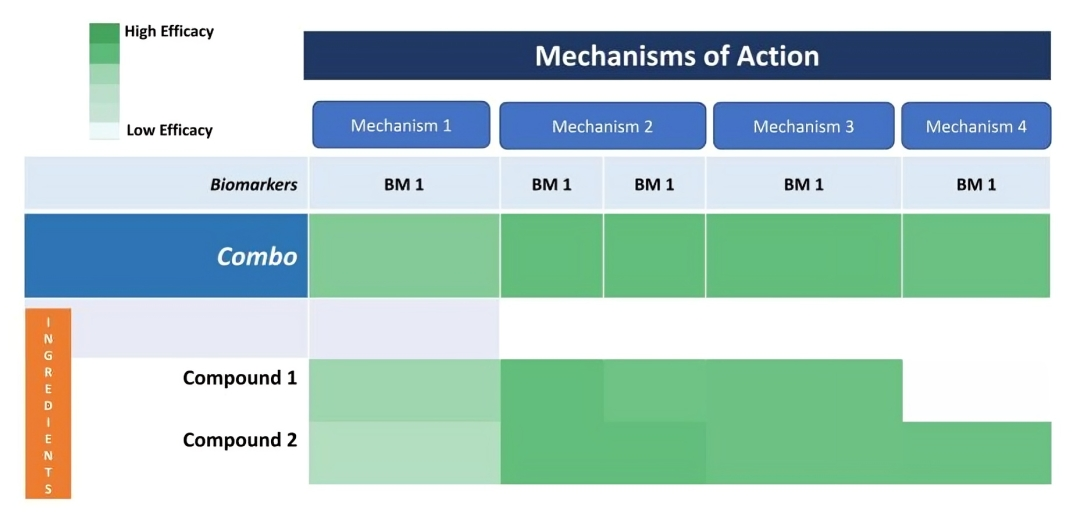
Combination Screening
In this Phase, natural ingredients were identified and selected to be combined that had optimal effect on the biomarkers . The dose levels of ingredients will be finalized in the optimal combination
Patents
The Open Science Institute® through its AML initiative is moving towards getting patents for a revolutionary compounds that affects cell proliferation and immune suppression activity.

Licensing and Manufacturing
The Osteoarthritis Initiative is in the “Licensing and Manufacturing” Phase. The Apigenin and Hesperidin combination is branded as “mV25™ – Momentum to moVe” and is available for purchase.
Please support this Phase by donating to the Osteoarthritis Initiative, signing up to become distributor of mV25™, or purchasing mV25™.
