Bowel health refers to the optimal functioning of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, particularly the colon and intestines, which play a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, and waste elimination.
Bowel health refers to the optimal functioning of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, particularly the colon and intestines, which play a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, and waste elimination. A healthy bowel ensures regular and comfortable bowel movements, maintains a balanced gut microbiome, and supports immune function. Several factors influence bowel health, including diet, hydration, physical activity, and stress levels. A fiber-rich diet—abundant in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes—supports healthy digestion by promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Adequate water intake is equally vital, as it softens stool and facilitates smooth passage through the intestines. The gut is home to trillions of beneficial bacteria that aid in breaking down food, producing essential nutrients like vitamin K and B12, and protecting against harmful pathogens. A balanced gut microbiota is critical not only for digestive health but also for regulating inflammation and supporting brain function via the gut-brain axis. Disruptions to bowel health may manifest as bloating, gas, constipation, diarrhea, or conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), or colorectal cancer. Long-term issues may arise from poor dietary habits, sedentary lifestyle, overuse of antibiotics, or chronic stress. Supporting bowel health involves lifestyle strategies such as consuming probiotics and prebiotics, staying physically active, managing stress, and limiting processed foods and alcohol. Regular screening and prompt attention to digestive symptoms are also essential for early detection of any abnormalities. A healthy bowel is foundational to overall well-being—affecting not just digestion but immunity, mood, and energy levels.
The Systems Architecture of Bowel Health is published as a web based tool open to public . Click below to interact with the Systems Architecture
A peer-reviewed paper from the Bowel Health Initiative will be published to the benefit of community. This phase is in progress.
In this phase, the Bowel Health Initiative will conduct in silico modeling to identify and test the efficacy of natural compounds against the Bowel diseases such as IBS, dysbiosis and colitis. This phase is yet to begin.
In this phase, combination screening will be performed to identify potential ingredient/compounds that target the biological process implicated in Bowel Health pathogenesis. This phase is yet to begin
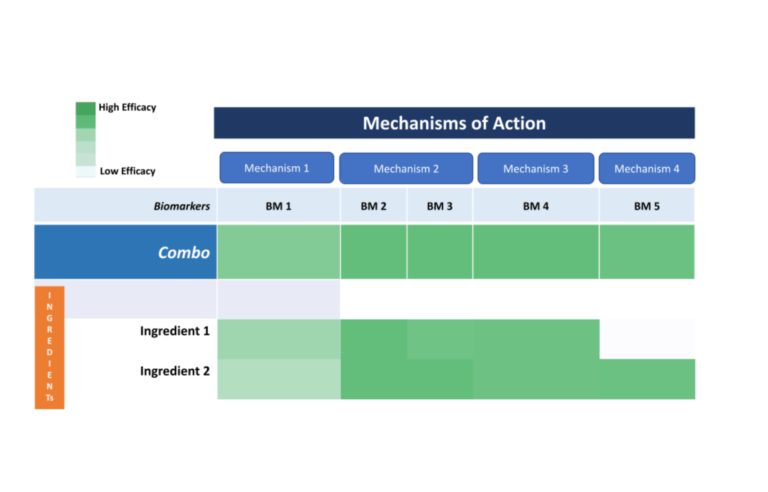
The Open Science Institute® through its Bowel Health Initiative is moving towards getting patents for a revolutionary molecule that effectively combats Bowel disease.
The Bowel Health Initiative plans to discover, develop, license and manufacture proprietary nutraceuticals to support treatment of Bowel Health. Support our mission to bring this innovation to those who need it most. Please support this phase by donating to the Bowel Health Initiative.

